A Regional Data Strategy for South East Wales - A Proposal
The Challenge:
The primary challenge lies in creating a Regional Data Strategy that aligns with the complex political landscape, including (at the time of writing) newly elected Labour UK Government, a long-standing Welsh Labour Government, and local strategic outcomes delivered through the Cardiff Capital Region and its local authority partners.
While the highest-level objectives are broadly similar, a detailed analysis of multiple strategies is required to align suitable, accessible, and achievable solutions that have a long-term, ongoing tangible benefit.
Developing solutions that understand the objectives of a complex political landscape with multiple competing agendas requires a strategic set of outcomes that can traverse the multiple stakeholders who have differing societal and economic outcomes based on the demographic, socioeconomic, and historical challenges that make up each local authority, which is accepted to be a complicated picture.
As a newly formed Corporate Joint Committee (CJC), the Cardiff Capital Region is a statutory body that has a broad remit from Transport, Energy, Sustainability, and Digital, with the focus on Economic Growth and Social Benefit . Any proposal will need to keep these strategic objectives at its core to ensure alignment to the outcomes of the CJC.

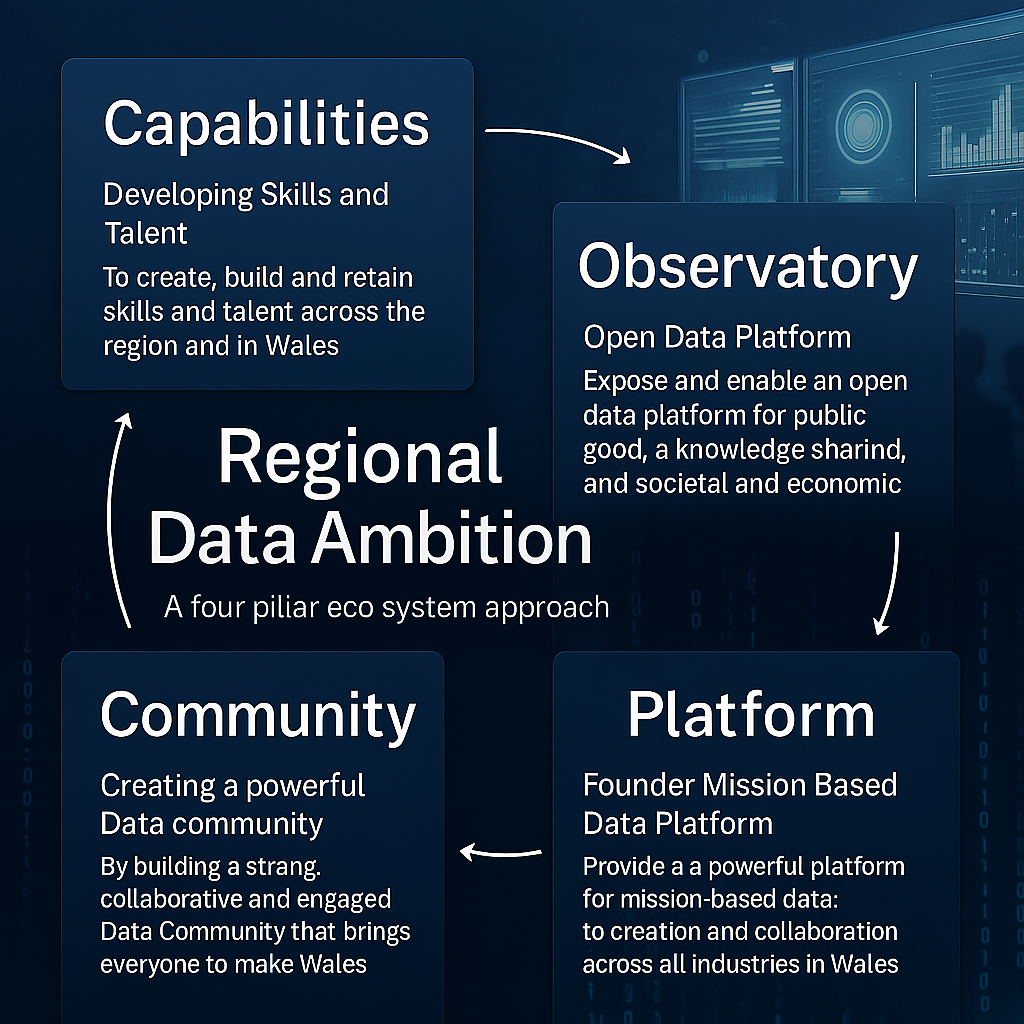
The Proposition: A Four-Pillar Ecosystem Approach (Regional Data Ambition Strategy)
The proposed Regional Data Ambition is a strategic approach to achieving the outcomes defined in the analysis of the multiple outcomes at various levels of Government, and other examples of where this approach has been successful across the World.
The concept is to build an ecosystem that empowers each individual component to reach its potential, or where appropriate to operate in isolation unless called upon . This approach intentionally decouples cost, risk, and resource with a view to providing the best value, and the best use of available skills, talent, and technology.
The ecosystem is made up of four components which are designed to run independently of each other; however, the true power of the ecosystem is that it should be able to call on each of the other components to enable and empower collaboration, co-creation, and partnership . Flexible, scalable technology is at the centre, providing data-enabled opportunities to realise complex solutions.
The four strategic components are:
Capabilities:
One of the critical outcomes of all strategies reviewed revolves around the need to offer skills and training within the Data space, with the strategic priority on Public Sector, Advanced Manufacturing, and Creative Industries . The power of the ecosystem supports this component by leveraging the experience of private sector organisations across the region to help support the delivery of real-world, local use cases of success.
Community:
The second component of the ecosystem is the proposal of a community-driven approach to Data where the requirements and innovation are driven by the members for the benefit of its members . Based on a community-first approach, the concept is to deliver a content platform that will enable two critical outcomes:
A content-driven social platform that will engage its members in co-creation, collaboration, and education through online, digital content.
A CPD (Continuing Professional Development) provision that will signpost, guide, and recommend academic and training opportunities to the community based on need, availability, and demand.
Observatory:
The third element of the ecosystem proposal is the delivery of a Data Observatory . The concept is to provide a solution that will centralise, standardise, and summarise disparate publicly available data through data visualisation, enabling and empowering citizens through usable and accessible data . With the added commercial opportunity to provide access to businesses to energise and improve the use of pertinent, trusted, accessible data . This proposal will look to provide a two-fold solution:
An external observatory that will look to address the strategic outcome of Data for Society and public good, exposing an automated visualisation of critical and beneficial data to enable end users to understand the current outputs from key datasets such as crime data, employment, health statistics, and economic measures to help inform businesses as to the benefits of the region.
An internally facing, secure and scalable solution that will provide a centralised, secure, flexible capability that consumes relevant data in order to help understand and inform policy decisions, enable regional reporting, provide advanced analytics capabilities and tools, and enable regional benefit reporting.
Mission Based Data Platform:
The fourth deliverable is a data platform specifically designed to bring together the ecosystem for the benefit of its members . This is a secure, flexible, and scalable solution that will provide a short-term power platform that can consume large amounts of data, empowering the secure access user base to deliver outcomes that are mission-focused and community-driven.
This capability, managed through an external partner with suitable and robust governance processes, can manufacture, engineer, and support the leveraging of data into a product or solution, and once completed, can delete, archive, or help to commercialise or productionise outcomes.
Aligning to the multi-mission based strategies, any data mission requires a platform that is capable of providing a value-for-money solution that is easily spun up and wound down as per the need, saving the need for an enduring platform, heavy investment in skills and technology, and the ability to drive innovation through technology without the long-term resource commitment to the regional stakeholders.
As an added benefit, to help deliver short-term, focused mission-based programmes such as Infuse, a component of the platform can be used for short-term, scaled projects, innovation, and prototyping, with a view to providing a high-specification solution that is low cost and flexible to the needs of CCR and its partners in the delivery of mission-focused social and economic outcomes.
Benefits:
Economic Growth: Data acts as an enabler for economic growth by:
- Driving Innovation: By harnessing data, businesses can innovate more effectively, leading to the development of new products and services, which can drive economic growth by creating new markets and opportunities.
- Improving Productivity: Data analytics can help identify inefficiencies and optimise processes within industries, improving productivity and contributing to economic growth.
- Informed Decision-Making: Data-driven decision-making allows policymakers and businesses to make more informed choices, leading to better resource allocation, targeted investments, and strategic planning that supports economic development.
- Supporting New Industries: Data is essential for the growth of emerging industries such as cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and the creative economy, as these sectors rely heavily on data to innovate and expand, driving economic growth.
- Enhancing Skills and Training: Data helps identify skills gaps and training needs, ensuring that the workforce is equipped with the necessary skills for the future economy, which can lead to higher employment rates and a more competitive economy.
- Inclusive Growth: By using data to understand and address regional disparities, the plan aims to ensure that economic growth benefits all parts of the country, leading to more balanced and sustainable economic development.
Societal Benefit: Data contributes to societal benefit by making trusted, quality data accessible and usable, which is central to meeting the strategic objectives of Government and Regional Data Strategy. Any provision will need to be able to provide a citizen-facing solution that provides meaningful data that benefits the people of the region . This includes:
- Economic Development: Data is used to shape economic policies and strategies, ensuring investments and initiatives are effectively targeted to stimulate growth and job creation, and helps identify opportunities for local businesses.
- Public Services Improvement: Data analytics improve the delivery of healthcare and social services by ensuring resources are allocated efficiently and services are tailored to meet the needs of the population, and identifies skills gaps to inform educational programmes.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Data is crucial for planning and optimising transport infrastructure, improving connectivity, and enhancing digital infrastructure.
- Environmental Sustainability: Data is used to monitor and improve energy efficiency, supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy and planning sustainable urban development.
- Community Wellbeing: Data analytics enhance public safety by identifying and addressing potential risks and improving emergency response systems, and helps identify and address social inequalities.

